| Authors: | Pieter Verding, Danny E.P. Vanpoucke, Yunus T. Aksoy, Tobias Corthouts, Maria R. Vetrano, and Wim Deferme |
| Journal: | Adv. Mater. Technol. XX, YY (2025) |
| doi: | 10.1002/admt.202502104 |
| IF(2025): | 6.2 |
| export: | bibtex |
| pdf: | <AdvMaterTechnol_XX> |
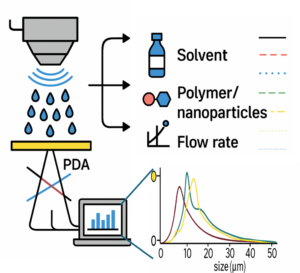 |
| Graphical Abstract: This study explores how machine learning models, trained on small experimental datasets obtained via Phase Doppler Anemometry (PDA), can accurately predict droplet size (D₃₂) in ultrasonic spray coating (USSC). By capturing the influence of ink complexity (solvent, polymer, nanoparticles), power, and flow rate, the model enables precise droplet control paving the way for optimized coatings in advanced functional materials. |
Abstract
This study examines droplet formation in ultrasonic spray coating (USSC) as a function of ink formulation (solvent, polymer, nanoparticles). First, acetone with polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) at concentrations from 0-4.5 wt% is used to examine the effect of polymer additions. Additionally, acetone-based SiO2 nanofluids (0-10 g/L), are explored. Finally, the combination of both polymer (PVDF) and nanoparticles (SiO2) in acetone is studied. Droplet sizes are measured using Phase Doppler Anemometry under varying atomization power and flow rates. Machine Learning (ML) algorithms are employed to develop droplet size models from key spray parameters, including atomization power, flow rate, polymer concentration, and nanoparticle concentration. The model shows significantly higher accuracy than existing empirical models. The model is further validated on IPA-based inks with polyethylenimine (PEIE) or ZnO nanoparticles, and on acetone–cellulose acetate formulations, confirming its robustness across diverse ink systems. In addition to revealing the influence of coating parameters on the droplet formation and distribution, obtained both via experimental validation and ML, this study demonstrates that ML can be effectively applied to small experimental datasets, offering a robust framework for optimizing droplet formation and understanding key spray parameters in USSC for complex, unexplored inks enabling novel coating applications.