| Authors: | Jarod J. Wolffis, Danny E. P. Vanpoucke, Amit Sharma, Keith V. Lawler, and Paul M. Forster |
| Journal: | Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 277, 184-196 (2019) |
| doi: | 10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.10.028 |
| IF(2019): | 4.551 |
| export: | bibtex |
| pdf: | <MicroporousMesoporousMater> |
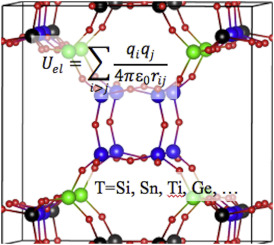 |
| Graphical Abstract: Partial charges in zeolites for force fields. |
Abstract
Partial atomic charge, which determines the magnitude of the Coulombic non-bonding interaction, represents a critical parameter in molecular mechanics simulations. Partial charges may also be used as a measure of physical properties of the system, i.e. covalency, acidic/catalytic sites, etc. A range of methods, both empirical and ab initio, exist for calculating partial charges in a given solid, and several of them are compared here for siliceous (pure silica) zeolites. The relationships between structure and the predicted partial charge are examined. The predicted partial charges from different methods are also compared with related experimental observations, showing that a few of the methods offer some guidance towards identifying the T-sites most likely to undergo substitution or for proton localization in acidic framework forms. Finally, we show that assigning unique calculated charges to crystallographically unique framework atoms makes an appreciable difference in simulating predicting N2 and O2 adsorption with common dispersion-repulsion parameterizations.